Electron Dot Notation For Sulfur
2.seven: Applications of Electron Configurations: Valence Electrons and Electron Dot Structures
- Page ID
- 214189
Valence Electrons
Every bit was mentioned in a previous department of this affiliate, electrons are highly important, because a specific subset of electrons, called valence electrons , are solely-responsible for determining how elements bail with one another. The number of valence electrons that are nowadays in an atom tin be determined from that atom'southward electron configuration. Valence electrons are establish in the orbitals associated with an atom's highest occupied energy level. The remaining electrons, which are called inner shell electrons, practice non participate in bonding and are, therefore, not important to study.
Consider sulfur'south electron configuration, which was determined in the previous section and is replicated below.
1 s ii two due south 2 2 p 6 3 s 2 3 p 4
Recall that the energy levels in an electron configuration are theleading red numbers that denote the first of a new energy level/orbital combination. Sulfur has electrons in the first, second, and 3rd energy levels, as indicated by the leading red ane, 2's, and 3'south, respectively. Valence electrons are those found in thehighest occupied energy level. Therefore, in this example, only those electrons associated with anenergy level/orbital combination start with a3 need to be considered. Since two energy level/orbital combinations brainstorm with a3, both orbitals are selected for further consideration:
3 s 2 3 p iv
The superscripts associated with these orbitals total to 6. Therefore, sulfur has 6 valence electrons.
While an electron configuration representsall of the electrons present in an cantlet of an chemical element, chemists are only truly interested in an atom'svalence electrons, since, as indicated above, those are the electrons that are solely-responsible for determining how elements bond with one another. Therefore, finding a "shortcut" for determining how many valence electrons are present in an atom would be highly convenient. Such a "shortcut" does, indeed, exist. In a previous section of this chapter, three systems for labeling the groups, or columns, on the periodic tabular array were presented. The second system, which is called the "A/B System," was indicated to provide insight into the electronic character of elements found within that group.
Once more, consider sulfur, S, which, based on its electron configuration, hasvi valence electrons.
Sulfur is located in the 16thursday column of the periodic table. However, the "A/B System" is used to label the chief group elements . Group 16 is the sixthursday cavalcade in the main group, or "A-Block," columns of the periodic table and so is labeled as Group half-dozen A . Annotation that sulfur'due south valence electron count matches its grouping number in the "A/B System." This connexion applies to nearlyall elements found in themain group columns of the periodic table. Helium is the simply exception to this rule, as it is found in Group 8A, but only contains two total electrons. This inconsistency invalidates the "A/B shortcut" method, and the electron configuration method must be employed to determine that both of helium'due south electrons are valence electrons.
Since the "A/B System" group number corresponds to the number of valence electrons that are nowadays in an atom, all elements found within the same column have the same number of valence electrons. Since an atom's valence electrons are solely-responsible for determining how elements bond with i another, this commonality in electronic character explains why all of the elements within the same group share like properties.
Electron Dot Structures
Electron dot structures surroundings the elemental symbol of an element with one dot for every valence electron that the chemical element contains. When drawing an electron dot construction, three rules must be followed:
- The first dot tin be placed on whatever "side" of the elemental symbol (top, bottom, left, or right).
- The start four dots must each be placed on their ain "side" of the elemental symbol. In other words, if the offset dot is placed on the top of the elemental symbol, the second dot can be placed on the bottom, left, or correct of the symbol, butcannot be placed at the top, aslope the first dot.
- The final four dots can again be placed on any "side" of the elemental symbol, but must be arranged such that no more than two dots be on any "side" of the elemental symbol.
Again, consider sulfur, which has 6 valence electrons.
The elemental symbol for sulfur is Due south. Since an electron dot construction surrounds an elemental symbol with one dot for everyvalence electron that the element contains, sulfur'south elemental symbol must be surrounded by 6 dots. Based on the rules given above, the dot representing sulfur'southward first valence electron can be placed on whatever "side" of the symbol, as shown beneath in Effigy \(\PageIndex{1}\).
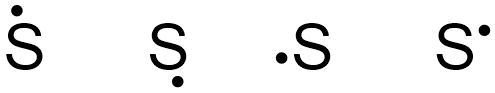
If the first structure in Figure \(\PageIndex{ane}\) is chosen as the ground of sulfur's electron dot structure, the dot representing sulfur's second valence electron can exist placed on the bottom, left, or correct of the elemental symbol, butcannot be placed at the top, alongside the first dot. Effigy \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows three structures with acceptable placements for sulfur's first ii valence electrons, also as a structure with an incorrect electron arrangement.
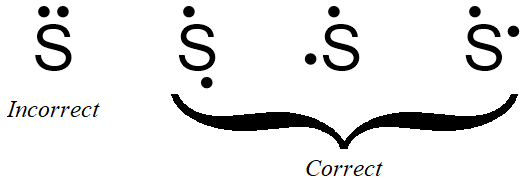
If the final construction in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) is called equally the basis of sulfur'southward electron dot structure, the dots representing sulfur'due south third and fourth valence electrons must be placed on the bottom and to the left of the elemental symbol, onlycannot be placed at the top or to the right of the elemental symbol. Effigy \(\PageIndex{iii}\) shows the only structure with an acceptable placement for sulfur'south starting time four valence electrons.
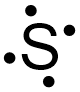
The dots representing sulfur'due south 5th and sixth valence electrons can once more exist placed on whatsoever "side" of the elemental symbol, but cannot both be placed on the same "side," and so that no more than 2 dots exist on any "side" of the elemental symbol. Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) shows all of the structures with acceptable placements for sulfur'due south six valence electrons. Therefore, any of the structures in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) is a valid electron dot construction for sulfur.
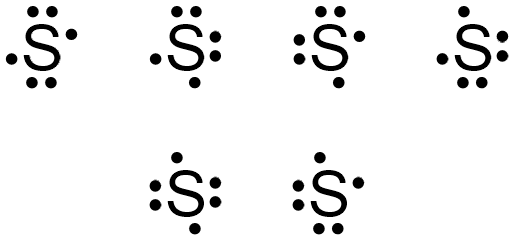
Electron Dot Notation For Sulfur,
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Heartland_Community_College/CHEM_120:_Fundamentals_of_Chemistry/02:_Atoms_and_Elements/2.07:_Applications_of_Electron_Configurations_Valence_Electrons_and_Electron_Dot_Structures
Posted by: weatherscoldnew.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Electron Dot Notation For Sulfur"
Post a Comment